Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a detection method based on in vitro antigen-antibody reaction, which combines antigen-antibody specific reaction with the efficient catalytic action of enzyme, and the sensitivity can reach the picogram (pg/mL) level. It is one of the most mature immunoassay methods for commercial application, and is widely used in medical experiments, clinical diagnosis, and biopharmaceuticals. Currently, there are four common types of ELISAs: bispecific antibody sandwich method, direct method, indirect method, and competitive method.

Among them, the bispecific antibody sandwich method is the most commonly used one, which is divided into double antibody sandwich and double antigen sandwich. The following small department will take the double antibody sandwich method as an example to share relevant knowledge with you~
Experimental Principle
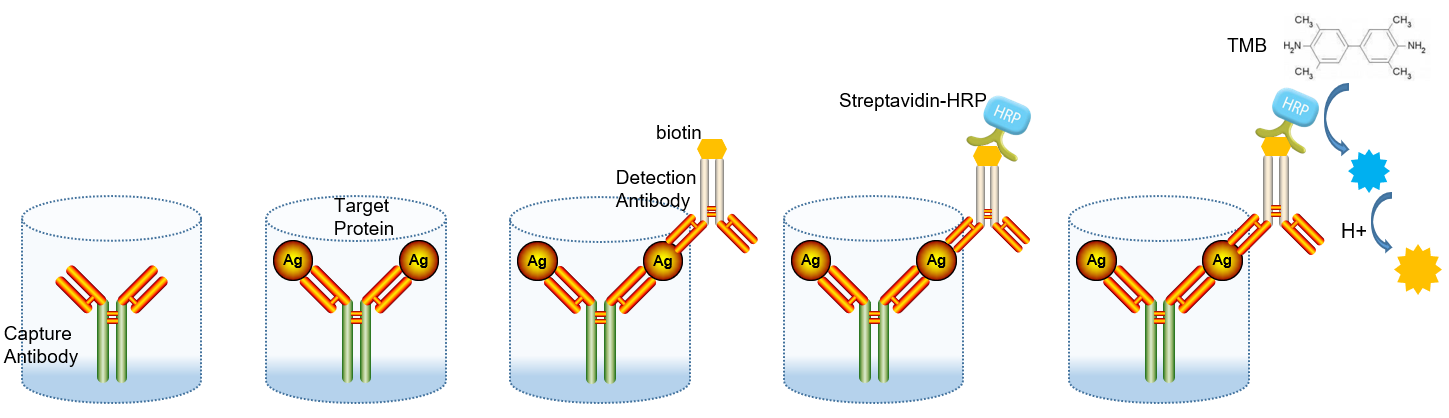
The basic principle of the double antibody sandwich method is to fix the quantitative coated antibody on the surface of the microplate by physical adsorption, and then add the specimen to be tested, and then use the TMB substrate to develop the color after the enzyme labeling the secondary antibody by adding the detection antibody, and the color shade in the microplate is positively correlated with the concentration of the analyte.
1 Coated Antibody
Many substances can be used as solid phase carriers, such as polyvinyl chloride, polystyrene, polypropylamide, and cellulose, and the microplate needs to be screened before antibody immobilization. From hydrophilic to hydrophobic, the binding of the microplate to the protein will change from strong to weak, resulting in a difference in adsorption capacity. When the antibody is adsorbed on the surface of the solid phase carrier, the purity is required, and the pH is generally required to be between 9.0~9.6 during adsorption. The optimal concentration of protein coating needs to be titrated: after coating with different protein concentrations, when other test conditions are the same, observe the OD value of the positive specimen, and select the concentration with the largest OD value and the least protein amount.
2 Standards and Samples
The standard is the pure protein of the target (the factor to be detected in the sample), and special attention needs to be paid to the dilution from the mother solution to the cascade dilution, and the production of the standard song is the key to the success of the ELISA experiment. The target to be tested needs to have multiple epitopes, i.e., bivalent or more bivalent macromolecular antigens, as this assay requires two antibodies. In addition, it is important to note that rheumatoid factor (RF) interference in serum samples can bind to the Fc moiety of denatured IgG in a variety of animals to produce false-positive reactions.
3 Washing Liquid
The ELISA procedure involves multiple plate washes. After a long period of incubation, non-specific binding will occur, and a wash solution is needed to wash away the non-specifically bound protein or antibody, usually PBS, 4-6 times, about 30 seconds each time. Multiple short washes are more effective than fewer long washes, and on the last wash, try to pat the liquid as much as possible while taking care to keep the board moist.
4 Detect Antibodies
In the double-antibody sandwich method, the binding site between the detection antibody and the target protein needs to be different from the binding site between the target and the coated antibody, which will involve the problem of antibody pairing. There are several commonly used antibody pairing methods:
- The coated antibody is a monoclonal antibody, and the detection antibody is a polyclonal antibody;
- The coated antibody is a monoclonal antibody, and the detection antibody is a monoclonal antibody, but the two monoclonal antibodies target different epitopes;
- coated antibody is a polyclonal antibody and the detection antibody is a polyclonal antibody, and the two types of polyclonal antibodies are generally derived from different hosts.
The
5 Biotinylated Secondary Antibodies
Due to the limitations of enzyme-labeled secondary antibodies, manufacturers now generally introduce a biotin avidin system (BAS), which is more convenient to apply while improving reaction sensitivity. When biotin labeling, the corresponding activated biotin and reaction conditions can be selected according to the type of labelable group (amino group, aldehyde group, sulfhydryl group, etc.) and the acidity and alkalinity of the molecule. After biotin labeling, it does not affect the biological activity of the labeled substance.
6 Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) - Labeled Avidin
Each avidin molecule binds to 4 biotin molecules, so more biotin-linked enzyme molecules can be coupled, greatly improving the sensitivity of ELISA experiments. The affinity between biotin and avidin is strong, and once combined, it is extremely stable, and this binding reaction time is shorter than that required for antigen-antibody reactions. Streptavidin "streptavidin, SA", which is a secretion during the culture of Streptomyces and consists of 4 identical peptide chains, is commonly used in the detection of BAS. HRP is sensitive, stable, high specific activity, small molecular weight, and the pure enzyme is easy to prepare. It has 4 pairs of cysteine-forming disulfide bonds, a salt bridge formed by Asp at 99 and Arg at 123, 9 potential glycosylation sites, and two metal centers that catalyze the production of the chromogenic substrate TMB to a blue monovalent.
7 Chromogenic Substrates
TMB (3,3',5,5'-tetramethylbenzidine) is widely used because it is more sensitive than other chromogenic substrates and is non-carcinogenic. HRP or other appropriate peroxidases can catalyze the formation of soluble blue in TMB in the presence of hydrogen peroxide, at which point absorbance can typically be determined at 370 nm. When the chromogenic reaction is terminated by an acidic solution, the product changes from a blue monovalent to a yellow bivalent, at which point the absorbance can be measured at 450 nm.
Summary of the Protocol
- Prepare all reagents and serial dilutions of standards. Add 300 μl of 1 × lotion to the slats and let stand and soak for 30 sec.
- Standard wells are added with 100 μl of 2-fold diluted standard. Serum/plasma: 100 μl of standard dilution is added to the blank wells; Cell culture supernatant: Add 100 μl of medium to the blank wells.
- Serum/plasma: 50 μl of 1× assay buffer and 50 μl of sample cell culture supernatant: 100 μl of cell culture supernatant is added to sample wells.
- Add 50 μl of 1:100 dilution of detection antibody to each well. Steps 2, 3, and 4 are completed within 15 minutes.
- Seal the film and incubate for 2 h at room temperature. Wash 6 times.
- Add 100 μl of horseradish peroxidase-labeled streptavidin at a 1:100 dilution per well.
- Seal the film and incubate for 45 min at room temperature. Wash 6 times.
- Add 100 μl of chromogenic substrate per well, protect from light, and incubate for 5-30 min at room temperature.
- Add 100 μl of stop solution per well.
- Within 30 minutes, the OD value is detected at 450 nm wavelength and the reference wavelength is 570 nm or 63 nm
Note: The above steps are based on Multi Sciences Biotech ELISA kits, the operation steps of different manufacturers' kits may be different, you must read the product instructions carefully before starting the experiment~
Easter Eggs
The ELISA method seems to be perfect, but there are inevitably some problems with practical applications. First, instead of a chemical connection between the plate and the antibody, the antibody is adsorbed on its surface by van der Waals forces, electrostatic attraction, hydrophobicity, and π-π packing. As a result, the plate cannot securely coat the surface of the antibody. After the subsequent incubation and plate washing process, it is inevitable that the adsorbed antibodies will be washed off, which increases the uncertainty of the experimental operation. Secondly, the recognition between the coated antibody and the antigen, and the detection of the existence between the antibody and the coated antibody is also more complex. Instead of one-to-one recognition between antibody antigens, one antigen can be linked to multiple antibodies, and one antibody can theoretically be linked to multiple antigens. The target and the detection antibody go through two recognition processes, which makes the recognition correspondence between the two more complicated. In this case, the detection signal and the concentration of the sample to be measured are no longer one-to-one. The use of 96-well plates in commercial assays is designed to eliminate some errors through multiple experiments. However, compared with conventional immunoassay experiments, ELISA has obvious advantages and can be described as the "gold standard" for protein quantification.